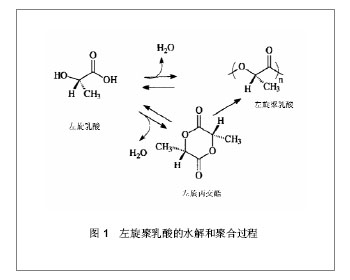
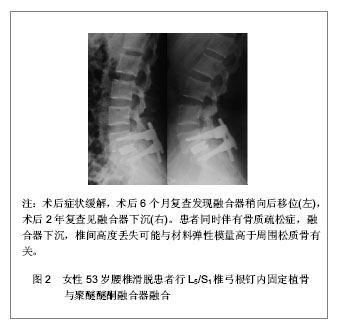
| [1] Mcafee PC,Cunningham BW,Lee GA,et al.Revision strategies for salvaging or improving failed cylindrical cages.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1999;24(20):2147-2153.
[2] Ohlin A,Karlsson M,Duppe H,et al.Complications after transpedicular stabilization of the spine. A survivorship analysis of 163 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1994;19(24): 2774-2779.
[3] van Dijk M,Smit TH,Sugihara S,et al.The effect of cage stiffness on the rate of lumbar interbody fusion - An in vivo model using poly(L-lactic acid) and titanium cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(7):682-688.
[4] 杨进顺,吕浩然,赵玉,等.不同类型椎间融合器的材料学特征及其临床应用效果[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(9): 1755-1757.
[5] Johnsson R,Axelsson P,Stromqvist B.Posterolateral lumbar fusion using facet joint fixation with biodegradable rods: a pilot study. Eur Spine J.1997;6(2):144-148.
[6] Deguchi M,Cheng BC,Sato K,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of translaminar facet joint fixation. A comparative study of poly-L-lactide pins, screws, and pedicle fixation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1998;23(12):1307-1313.
[7] Vaccaro AR.Bioabsorbable screws.J Neurosurg Spine.2011; 15(4):359-360.
[8] Daniels AU,Chang MK,Andriano KP. Mechanical properties of biodegradable polymers and composites proposed for internal fixation of bone.J Appl Biomater.1990;1(1):57-78.
[9] Lohfeld S,Cahill S,Barron V,et al.Fabrication, mechanical and in vivo performance of polycaprolactone/tricalcium phosphate composite scaffolds. Acta Biomater.2012;8(9):3446-3456.
[10] Chunguang Z,Yueming S,Chongqi T,et al.Evaluation of bioabsorbable multiamino acid copolymer/alpha-tri-calcium phosphate interbody fusion cages in a goat model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2011;36(25):E1615-E1622.
[11] 周春光,宋跃明,屠重棋,等. 多元氨基酸共聚物/磷酸钙复合材料椎间融合器的设计制备及压缩强度测试[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2011,28(4):1136-1140.
[12] Wuisman PI,Smit TH.Bioresorbable polymers: heading for a new generation of spinal cages.Eur Spine J.2006;15(2): 133-148.
[13] Bowlin GL.Encyclopedia of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering. 2nd ed. ed. 2008:1254-1264.
[14] Hutmacher DW,Schantz T,Zein I,et al.Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling.J Biomed Mater Res.2001;55(2):203-216.
[15] Gautier SE,Oudega M,Fragoso M,et al. Poly(alpha-hydroxyacids) for application in the spinal cord: resorbability and biocompatibility with adult rat Schwann cells and spinal cord.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;42(4):642-654.
[16] Claes L,Ignatius A.Development of new, biodegradable implants. Chirurg. 2002;73(10):990-996.
[17] Gautier SE,Oudega M,Fragoso M,et al. Poly(alpha-hydroxyacids) for application in the spinal cord: resorbability and biocompatibility with adult rat Schwann cells and spinal cord.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;42(4):642-654.
[18] Smit TH.The use of a quadruped as an in vivo model for the study of the spine - biomechanical considerations.Eur Spine J.2002;11(2):137-144.
[19] Smit TH,Muller R,van Dijk M,et al.Changes in bone architecture during spinal fusion: three years follow-up and the role of cage stiffness. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003; 28(16):1802-1809.
[20] Debusscher F,Aunoble S,Alsawad Y,et al.Anterior cervical fusion with a bio-resorbable composite cage (beta TCP-PLLA): clinical and radiological results from a prospective study on 20 patients.Eur Spine J.2009;18(9): 1314-1320.
[21] Lippman CR,Hajjar M,Abshire B,et al.Cervical spine fusion with bioabsorbable cages.Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E4.
[22] Kandziora F,Pflugmacher R,Scholz M,et al.Bioabsorbable interbody cages in a sheep cervical spine fusion model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(17):1845-1856.
[23] Lazennec JY,Madi A,Rousseau MA,et al. Evaluation of the 96/4 PLDLLA polymer resorbable lumbar interbody cage in a long term animal model. Eur Spine J.2006;15(10): 1545-1553.
[24] Lyons AS,Sherman BP,Puttlitz CM,et al.Failure of resorbable plates and screws in an ovine model of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine J.2011;11(9):876-883.
[25] Coe JD,Vaccaro AR.Instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bioresorbable polymer implants and iliac crest autograft.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(17 Suppl): S76-S83.
[26] Abbah SA,Lam CX,Hutmacher DW,et al.Biological performance of a polycaprolactone-based scaffold used as fusion cage device in a large animal model of spinal reconstructive surgery.Biomaterials.2009;30(28):5086-5093.
[27] Ergun A,Chung R,Ward D,et al.Unitary bioresorbable cage/core bone graft substitutes for spinal arthrodesis coextruded from polycaprolactone biocomposites. Ann Biomed Eng.2012;40(5):1073-1087.
[28] Lowe TG,Coe JD.Bioresorbable polymer implants in the unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion procedure. Orthopedics.2002;25(10 Suppl):s1179-s1183, s1183.
[29] Couture DE,Branch CJ. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with bioabsorbable spacers and local autograft in a series of 27 patients. Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E8.
[30] Kuklo TR,Rosner MK,Polly DJ.Computerized tomography evaluation of a resorbable implant after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E10.
[31] Coe JD.Instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bioabsorbable polymer implants and iliac crest autograft.Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E11.
[32] Lanman TH,Hopkins TJ. Early findings in a pilot study of anterior cervical interbody fusion in which recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 was used with poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) bioabsorbable implants. Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E6.
[33] Frost A,Bagouri E,Brown M,et al.Osteolysis following resorbable poly-L-lactide-co-D, L-lactide PLIF cage use: a review of cases. Eur Spine J.2012;21(3):449-454.
[34] Jiya TU,Smit T,van Royen BJ,et al.Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using non resorbable poly-ether-ether-ketone versus resorbable poly-L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide fusion devices. Clinical outcome at a minimum of 2-year follow-up.Eur Spine J.2011;20(4):618-622.
[35] Thomas KA,Toth JM,Crawford NR,et al.Bioresorbable polylactide interbody implants in an ovine anterior cervical discectomy and fusion model: three-year results. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(7):734-742.
[36] Kandziora F,Pflugmacher R,Scholz M,et al.Comparison between sheep and human cervical spines: an anatomic, radiographic, bone mineral density, and biomechanical study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(9):1028-1037. |